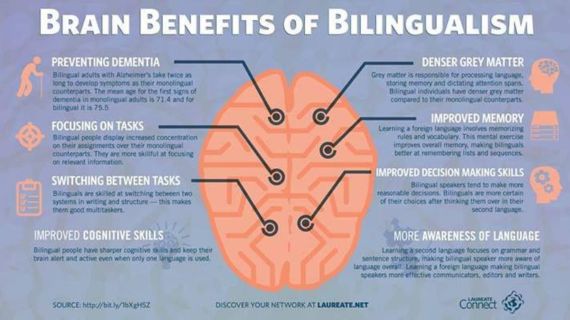
Learning foreign languages offers significant cognitive benefits that are accessible to individuals of all age groups. Research has consistently shown that language learning enhances memory, improves problem-solving skills, boosts cognitive flexibility, and enhances overall brain function. These benefits extend beyond linguistic proficiency and contribute to cognitive abilities in various domains, such as attention, executive functions, and multitasking. Furthermore, language learning has been associated with a delay in age-related cognitive decline and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative disorders. Whether starting early in childhood or embarking on language learning in adulthood, the cognitive advantages are tangible and provide lifelong benefits to individuals willing to explore the world of foreign languages.
0 Comment
Continue Reading →
Selecting the 10 most effective study habits for foreign language learning is a matter of personal choice and experience. If we were to ask a dozen experienced learners to make such a list, certainly there would be significant differences among individual habits chosen. Here I make a judgment call based on more than 5 decades of studying 47 languages and achieving reasonable levels of communicative competence in over 30 of them.
It is possible to have a basic understanding of a language without knowing its culture but to fully understand a language, one needs to have some understanding of the culture that produced it.